Carbon capture processes
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Carbon capture is a process that can remove as much as 90% of the carbon dioxide (CO2) gas emitted from fossil fuel (coal, oil or gas) power stations which are the main source of anthropogenic CO2 emissions. But the process is also used in cement making and other industries, and can be used to extract carbon from the atmosphere.
Carbon capture has been used for decades by the oil and gas sectors, although long-term storage of CO2 is a relatively new activity. It is thought that carbon capture could achieve around 20% of the total greenhouse gas emissions reductions needed to achieve 2050 targets. It is seen as one of the few practical ways to efficiently decarbonise the industrial sector quickly.
[edit] Carbon capture and storage (CCS)
CO2 captured from industrial processes is captured for secure and indefinite storage. In the UK storage of large quantities of CO2 is likley to take place in offshore underground saline formations or depleted oil and gas fields.
Although at the time of writing there are around 17 operating CCS projects globally, there are no commercial-scale CCS projects in the UK, but relevant health and safety regulations exist for future operators to abide by.
There are three stages to carbon capture and storage:
- CO2 is trapped and separated from other gases.
- CO2 is transported to a storage site.
- CO2 is stored away from the atmosphere.
[edit] Trapping and separating CO2
There are three ways to extract CO2:
- Post-combustion capture - applied mostly to power plants, post-combustion capture involves capturing the CO2 from the flue gases produced by fossil-fuel combustion. Typically, chemical solvents are used to achieve this. The technology can be retrofitted to existing power plants.
- Pre-combustion - this process involves removing the CO2 before combustion takes place in chemical, fertilizer, gaseous fuel and power production processes. Rather than being combusted, fuel is ‘gassified’ to produce a synthetic gas (syngas). The carbon monoxide (CO) from this is converted to CO2 which, after the action of solvents, is freed from the hydrogen present.
- Oxy-fuel combustion - fossil fuel is burned in oxygen to produce a steam-CO2 mixture from which the CO2 is separated by cooling and compression. This is a relatively expensive process becuase of the amount of oxygen required, however it ensures that only around 10% of a power plant’s emissions enter the atmosphere.
It may also be possible to extract CO2 from ambient air (direct air capture), although it is more difficult than the aforementioned processes due to the lower concentration of the gas in air. Work on this is still at an early stage.
[edit] Transportation of CO2
Once captured, CO2 must be transported to suitable sites for permanent storage. Conveyance is mostly by pipeline as this is one of the cheapest methods for large volumes. CO2 can also be transported – eg by ships – to other locations for industrial use.
[edit] Storing CO2
The three techniques available for storing CO2 are:
- In deep geological formations.
- In deep ocean water.
- In the form of mineral carbonates (mineral storage).
For more information see: http://www.bgs.ac.uk/discoveringGeology/climateChange/CCS/howcanCO2bestored.html
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Carbon dioxide capture and utilisation.
- Carbon capture and storage.
- Carbon emissions.
- Carbon footprint.
- Carbon Reduction Commitment Energy Efficiency Scheme.
- Climate change act.
- Climate change science.
- Government publishes 2021 guidance on carbon capture technologies.
- Greenhouse gases.
- Environmental impact.
- Ozone depleting substances.
- UK Climate Change Risk Assessment.
- Using CO2 to make construction products and materials.
Featured articles and news
Twas the site before Christmas...
A rhyme for the industry and a thankyou to our supporters.
Plumbing and heating systems in schools
New apprentice pay rates coming into effect in the new year
Addressing the impact of recent national minimum wage changes.
EBSSA support for the new industry competence structure
The Engineering and Building Services Skills Authority, in working group 2.
Notes from BSRIA Sustainable Futures briefing
From carbon down to the all important customer: Redefining Retrofit for Net Zero Living.
Principal Designer: A New Opportunity for Architects
ACA launches a Principal Designer Register for architects.
A new government plan for housing and nature recovery
Exploring a new housing and infrastructure nature recovery framework.
Leveraging technology to enhance prospects for students
A case study on the significance of the Autodesk Revit certification.
Fundamental Review of Building Regulations Guidance
Announced during commons debate on the Grenfell Inquiry Phase 2 report.
CIAT responds to the updated National Planning Policy Framework
With key changes in the revised NPPF outlined.
Councils and communities highlighted for delivery of common-sense housing in planning overhaul
As government follows up with mandatory housing targets.
CIOB photographic competition final images revealed
Art of Building produces stunning images for another year.
HSE prosecutes company for putting workers at risk
Roofing company fined and its director sentenced.
Strategic restructure to transform industry competence
EBSSA becomes part of a new industry competence structure.
Major overhaul of planning committees proposed by government
Planning decisions set to be fast-tracked to tackle the housing crisis.
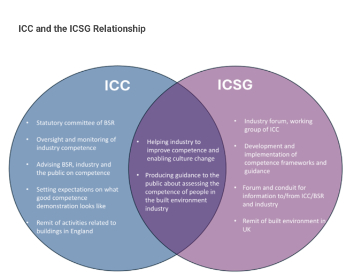
Industry Competence Steering Group restructure
ICSG transitions to the Industry Competence Committee (ICC) under the Building Safety Regulator (BSR).
Principal Contractor Competency Certification Scheme
CIOB PCCCS competence framework for Principal Contractors.
The CIAT Principal Designer register
Issues explained via a series of FAQs.